What is an Air Cylinder? Structure, Operating Principle, Types, Selection Points, and Applications for Each Process
Air cylinders are pivotal elements in industrial machinery and automation systems. Their straightforward construction and high resilience enable widespread use across various applications. This section introduces the basic features and types of air cylinders, and explains in detail how to use the advantages of air cylinders in each actual manufacturing process.
- 1.What is an Air Cylinder?
- 2.Principle of Air Cylinder Operation
- 3.Types of Air Cylinders
- 4.Air Cylinder Selection Points
- 4-1.Cylinder Bore Size
- 4-2.Mounting Style
- 4-3.Cylinder Stroke
- 4-4.Speed
- 4-5.Cushion Capacity
- 4-6.Ambient Temperature, Atmosphere
- 5.Characteristics of Air Cylinders
- 5-1.Advantages of Air Cylinders
- 5-2.Disadvantages of Air Cylinders
- 5-3.Drive Components other than Air Cylinders
- 6.CKD recommends the following points for utilizing air cylinders in specific processes
- 6-1.Handling Process
- 6-2.Conveying Process
- 6-3.Clamping process
- 6-4.Press-Fitting Process
- 6-5.Oscillating Process
- 7.CKD Air Cylinders
What is an Air Cylinder?
An air cylinder is a device that utilizes compressed air as its power source. It plays a crucial role in automation and efficiency enhancement within factories by converting compressed air energy into linear or reciprocating motions.
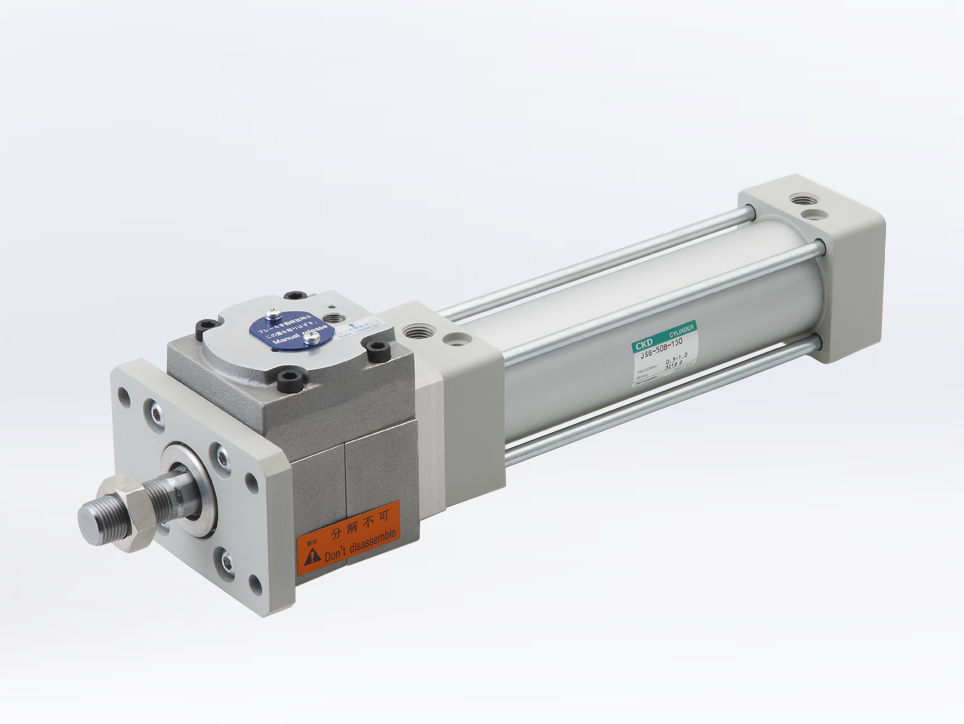
Structure of Air Cylinders
Outlined below are the primary components of an air cylinder:
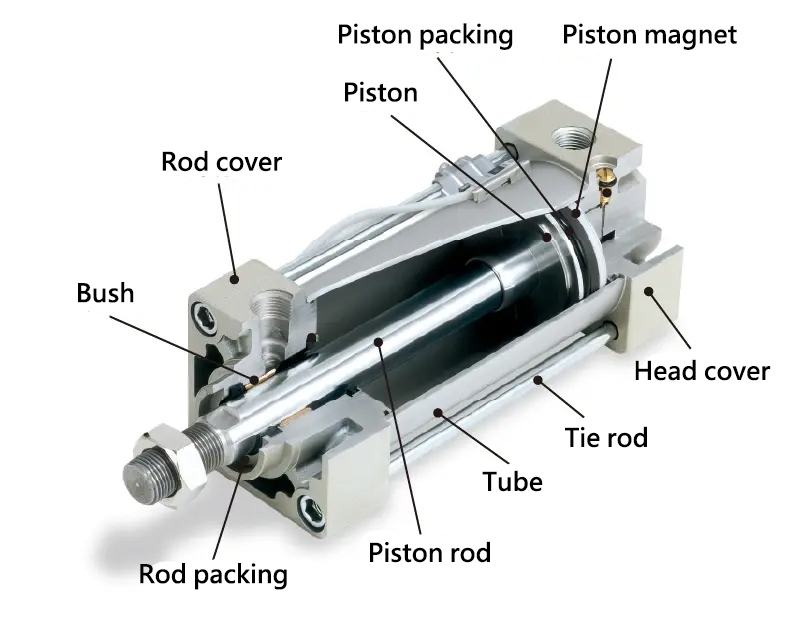
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Cylinder tube: | Forms the cylinder chamber. It also serves as the guiding track for the piston's sliding action (*). |
| Cover: | This component, housing supply and exhaust ports, forms the cylinder chamber. It is split into head and rod covers. |
| Tie Rod: | Connects the cylinder tube to the cover, securing them together. |
| Piston: | Propelled by air pressure, it moves within the cylinder tube. |
| Piston Packing: | Seals the interior of the cylinder to prevent air leaks. |
| Piston Magnet: | Serves as a detectable feature for cylinder switches. |
| Piston Rod: | Transmits the force and displacement of the piston externally. |
| Rod Packing: | Seals the space around the piston rod to avoid air loss. |
| Bush: | Provides a guiding function for the piston rod's sliding motion. |
※Note: "Sliding" refers to the gliding movement within the cylinder.
Principle of Air Cylinder Operation
Push Operation: Introducing compressed air through the cylinder's head port propels the piston, pushing the piston rod outward, while the pressurized air on the rod side is vented to the atmosphere.
Pull Operation: Introducing compressed air via the rod side port causes the piston to retract, which pulls the piston rod inward. Simultaneously, the air previously pressurized in the head side chamber is released to the atmosphere.
Types of Air Cylinders
Air cylinders are essential for automation and labor saving, but what types are there? The following is an explanation of five typical types.
General type
The general type air cylinder has a cylindrical body and is the most widespread design.This simple design makes them cost-effective and allows them to be versatile.

Space-Saving type
Space-saving air cylinders have a shorter stroke than the standard type and can be utilized in confined spaces due to their compactness and lightness. They are also affordable, allowing them to be widely used in large production volumes.

Guided type
The guided type is an air cylinder in which the piston performs precise linear motion with the use of a guide. The presence of the guide enables the piston to move stably. This type is particularly suitable for operations requiring precise linear movement or when the application involves aligning components with exactness. It is also recommended for scenarios where the piston rod is subject to lateral forces during operation.

With Brakes (Lock) type
A brake is added to the standard air cylinder, allowing the piston to stop at a specific position. This function is used in situations where stopping at a specific position is required or as a safety measure in the event of power supply trouble, etc.

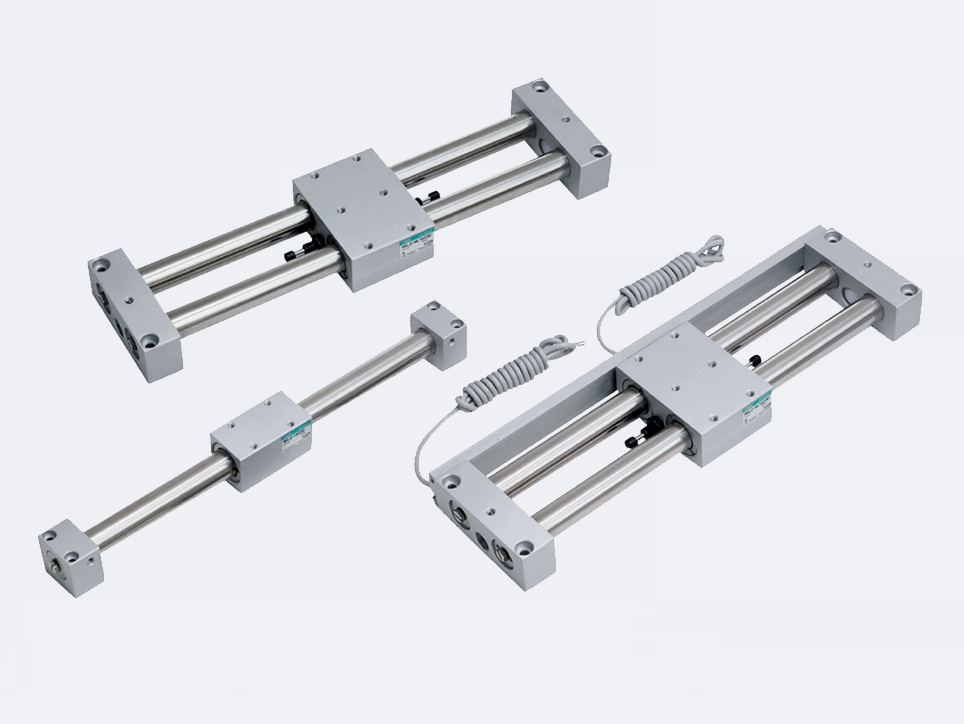
Rodless type
Since the rodless air cylinder does not have a rod, the total length is short, saving space. It also supports very long strokes, making it suitable for use in situations where objects need to be moved or their length minimized.

Air Cylinder Selection Points
There are many types of air cylinders, and they must be selected appropriately according to the purpose and conditions of use. Here we explain the main points for selection.
Cylinder Bore Size
The thrust of an air cylinder is calculated by "the product of the pressure-receiving area of the cylinder piston and the supply pressure," and is called the theoretical thrust. The effective thrust, which is obtained by multiplying this theoretical thrust by the safety factor (load factor), must be greater than or equal to the thrust required to move the load on the cylinder (load). The load factor is generally set to 30 to 70% to ensure safe and reliable operation according to the supply pressure and load direction.
Mounting Style
Air cylinder mounting styles can be broadly classified into "fixed type" and "oscillating type. With the fixed type, the cylinder body is fixed and the piston rod moves on the Main body shaft center. In the oscillating type, the cylinder body is not fixed but supported by a movable shaft so that it can oscillate and follow the movement of the workpiece.
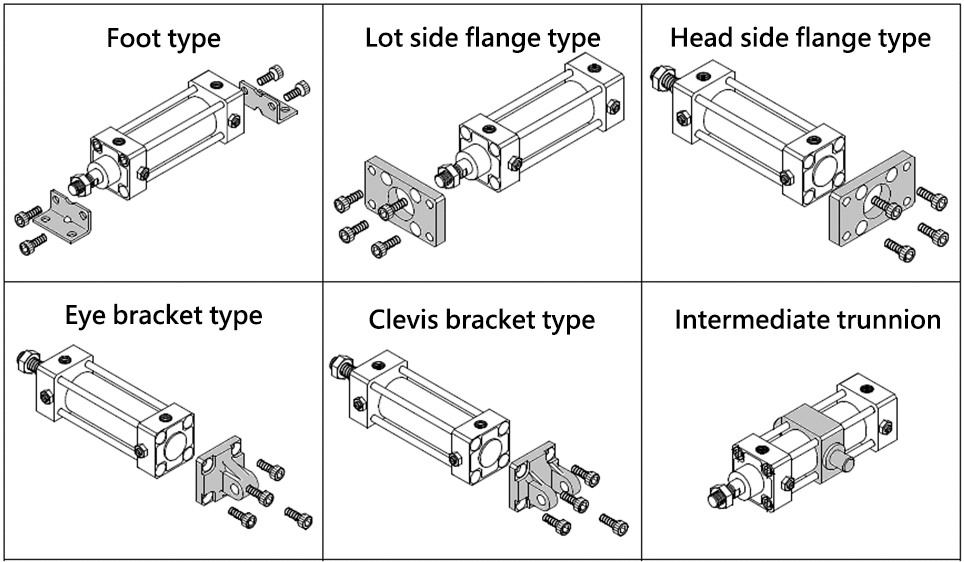
By selecting a suitable bracket according to the direction of load movement, the operation of the air cylinder can be smoothed and the service life can be extended.
Cylinder Stroke
The cylinder stroke that can be manufactured varies with the type of air cylinder and the inner bore size. A longer stroke increases the buckling force on the air cylinder body and piston rod. The maximum stroke varies depending on the load conditions, piston rod end, and mounting style, so confirmation is required. If a lateral load is applied to the piston rod, it is necessary to adopt an air cylinder that can handle the lateral load, use a free joint, and reconsider the mounting support fittings.
Speed
The speed at which an air cylinder can be used also differs depending on the type of air cylinder. Air cylinders that can be used at high speeds are equipped with a cushioning mechanism that can absorb the large inertial forces generated during movement. Conversely, if an air cylinder is moved at low speed, it will operate unsteadily due to the characteristics of air and sliding resistance, so it is necessary to select a low-speed type air cylinder with countermeasures against this problem. Also important is system selection (valves, speed controllers, silencers, etc.) to ensure the necessary air volume to operate the air cylinder at a given speed.
Cushion Capacity
As the air cylinder piston speed increases, impact force is generated when it hits the cover at the final end of the piston, so it is necessary to check the cushioning capacity to prevent damage. In particular, a large load inertia force may lead to damage. Selecting an air cylinder with cushioning capability to absorb impact can increase the durability of the air cylinder and the machine as a whole. If a shock exceeding the cushioning capacity of the air cylinder is anticipated, an external shock absorber or similar device should be installed to absorb the shock.
Ambient Temperature, Atmosphere
Ambient temperature and atmosphere affect cylinder performance and durability. In high or low temperatures, dusty environments, or environments where cutting oil is present, it is important to select cylinders with materials and mechanisms suitable for these conditions.
Many of the selection points introduced here may be easily selected by referring to the selection software available on our website or the system tables in our catalogs, so please take advantage of them.
Characteristics of Air Cylinders
Advantages of Air Cylinders
Lightweight: Air cylinders with simple mechanisms are lightweight, which reduces the load on the actuator or robot to which the air cylinder is attached, enabling size reduction.
Compact and High Thrust:Compared to electric actuators, air cylinders are compact and can be installed in limited space. Another feature of this type of actuator is that it can generate high thrust in spite of its compact size.
High-speed drive: High speed operation is possible by adjusting the air flow rate.
Low Cost: Relatively low manufacturing costs keep initial costs low when investing in equipment.
Easy Maintenance:The simple mechanism of air cylinders allows for easy maintenance and low operating costs. If the recently released High-Durability Component HP Series is adopted, the service life of the air cylinder will be longer, and the number of maintenance cycles can be greatly reduced.
Disadvantages of Air Cylinders
Because they use air, a compressible fluid, they have disadvantages such as difficulty in precise speed and position control, and are easily affected by load.
Drive Components other than Air Cylinders
Electric actuators are available to compensate for the disadvantages of air cylinders. Since the operation of air cylinders is basically limited to movement between two points, precise position control at multiple points is difficult. Electric actuators are products that combine mechanical parts with a motor that uses electricity as the power source. Compared to air cylinders, electric actuators are generally more expensive and tend to be larger in size, but the motor has excellent controllability, enabling precise position control at multiple points and shock mitigation control at the end of the stroke.
CKD recommends the following points for utilizing air cylinders in specific processes
In this section, we will compare the recommended points for using air cylinders for each actual manufacturing process in comparison to electric actuators.
Handling Process
The handling process is the process of gripping (grasping) a workpiece.
Recommended points of air cylinders!
・Lightweight
A lighter hand reduces the load on the actuator and robot for conveyance and allows for size reduction. For the same gripping force, we recommend a lightweight air hand.
・Compact and High Thrust
Air hands are more compact than electric actuators.When an air hand is attached to an actuator for conveyance or a robot, the moment of inertia, which is considered in the selection of the actuator, can be lowered.
・Wide Range of Variations
A wide range of variations allows the selection of the Air hand that best suits the workpiece.
Conveying Process
The conveying process is the process of transferring the handled workpiece.It is recommended for transferring between two points.
Recommendations for Air Cylinders!
・Range of Payload Coverage
Air cylinders have a higher payload capacity than electric actuators, and the payload capacity does not decrease with speed. Air cylinders are recommended when heavy workpieces need to be moved quickly.
・Vertical Transfer
Air cylinders excel at long, high-speed, and vertical transfers.Vertical transfer does not change the payload capacity.
Clamping process
The clamping process is a process that fixes the workpiece temporarily on the line for press fitting, inspection, assembly, etc.
Recommended points of Air Cylinders!
・Quick Operation
Clamps should be operated quickly for the next process. Air cylinders have a short actuation time, contributing to shorter equipment tact time.We recommend a compact and low-cost air cylinder with high clamping force.
・Energy Saving
Even if the clamping time is longer, power consumption does not increase. Electric actuators consume power during clamping, but once air pressure is supplied to the air cylinder, it is maintained, so power consumption does not change even if the clamping time is lengthened.
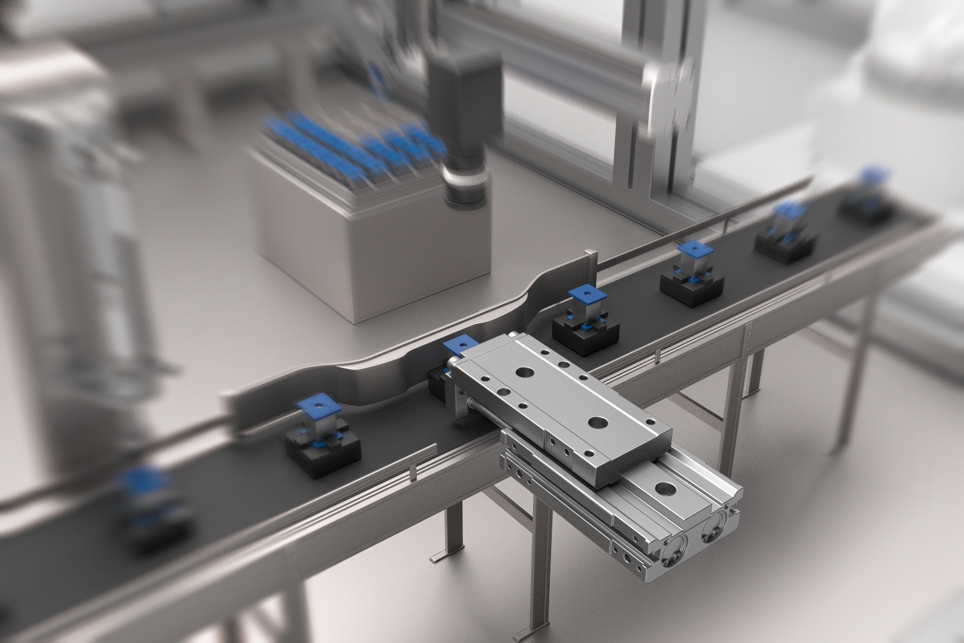
Press-Fitting Process
The press-fit process is a process in which a bar-shaped workpiece is pressed into another workpiece with a hole by applying pressure.
Recommended points for Air Cylinders!
・Compact and High Thrust
In the press fitting process, compactness and high pushing force are desired.Air cylinders are compact, have high pushing force, and are low cost. They are also easy to connect to external guides and can be easily reinforced.
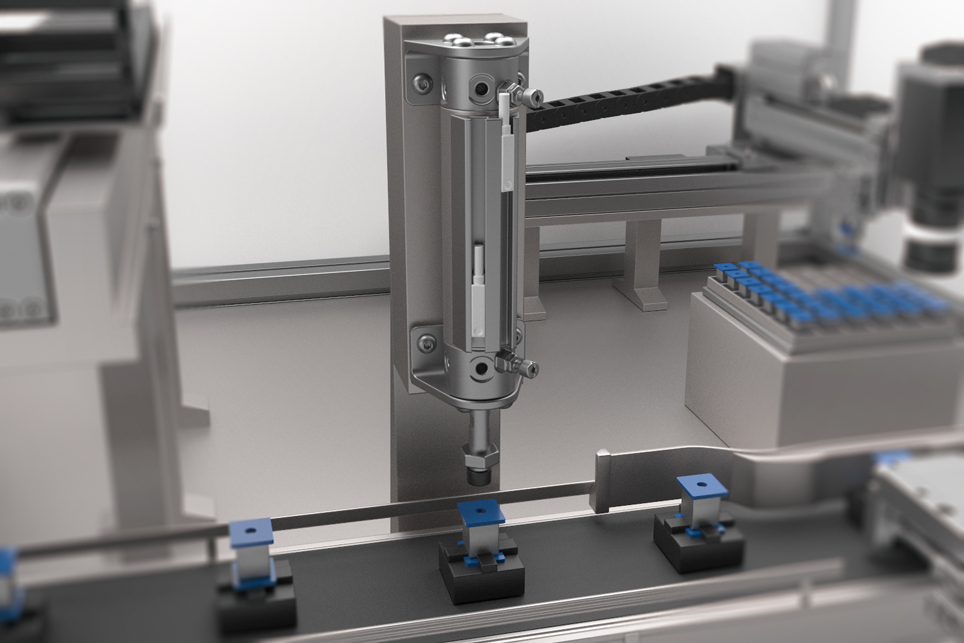
Oscillating Process
Oscillating is a motion of repeatedly turning between two points at a predetermined angle, like a pendulum. It is used for Pick & Place applications such as feeding workpieces from a conveyor to an inspection table.
Recommended points for Air Cylinders!
・High-Speed Rotation
High-speed movement is desired for oscillating conveyors. Air cylinders can move at high speeds even at 180° rotation, and we recommend air cylinders because of their low initial cost.
CKD Air Cylinders
Supporting System Automation in Industrial Fields
At CKD, our offerings extend beyond air cylinders, favored across various industries for their affordability and automation simplicity, to a comprehensive product lineup. This lineup includes electric actuators, direct drive motors, index cam units, and auxiliary devices, all designed to enable flexible operations and support the mass customization of production facilities, thus bolstering manufacturing worldwide.
High Durability Component HP Series
The High-durability Component HP Series is a long-life air cylinder designed to ensure "non-stop production equipment" and "stable operation. By extending the service life of air cylinders, the number of maintenance cycles can be drastically reduced, and this product also contributes to the reduction of waste generated when replacing air cylinders. This one-step-ahead air cylinder enables us to offer differentiated proposals that also lead to carbon neutrality.
Air & Electric Motion: Best Mix
CKD develops and manufactures both air cylinders and electric actuators. We can propose the best of both air and electric actuators based on a total assessment of the functions and cost of each.