What is an electric actuator? Overview of Electric Actuators: Types, Selection Methods, and Application in Processes
Driven by the global emphasis on environmental issues and CO2 reduction, the transition towards electrification is encroaching upon areas traditionally dominated by pneumatic equipment, namely actuators. Electric actuators not only offer the advantage of lower energy costs but also possess numerous benefits, such as the ability to perform multi-point positioning mid-stroke and adjust the gripping force of chucks. In this discussion, we will elaborate on the general overview of electric actuators, their types, and the advantages of electric actuators over air cylinders.
- 1.What is an electric actuator?
- 2.Types of electric actuators
- 3.Criteria for Selecting Electric Actuators
- 4.Characteristics of Electric Actuators
- 5.CKD's Recommended Selection Method for Electric Actuators by Process
- 5-1.Handling Process
- 5-2.Conveying Process
- 5-3.Clamping process
- 5-4.Press-Fitting Process
- 5-5.Oscillating Process
- 6.CKD's Electric Actuators
What Are Electric Actuators?
Electric actuators are a fundamental mechanical element within industrial machines and automation systems. They transform the rotational force of electric motors into linear or rotary motion to control position, speed, torque, etc., across various industrial applications.
Basic Mechanism of Electric Actuators
Electric actuators primarily consist of motors and transmission mechanisms. Stepper motors and servo motors are mainly used as motors. Since the rotational angle of the motor can be controlled, stroke can be performed at any point even in the middle of the positioning.
The transmission mechanism converts the motor’s rotational force into movement. For linear motion electric actuators, ball screws and linear guides are typically employed. Ball screw converts the rotational force of the motor to the linear motion of the piston rod or slider. The linear guide is a piston rod or a part that ensures the linear performance of the slider. In rotary electric actuators, gears and belts are commonly used as transmission mechanisms. Gears directly convert motor rotation into rotary motion, whereas belts provide a quiet and smooth transfer of the motor’s rotational force.
Types of electric actuators
Electric actuators are categorized into those with motors and those without motors. Motorized actuators have built-in motors, whereas non-motorized ones come without motors, allowing for the addition and control of familiar motors from various manufacturers.Motorized versions are divided into stepper motor-driven types and servo motor-driven types. Since the stepping motor drive type is driven by small teeth (step) stamped on the outer peripheral side and moves at a constant angle at each step, precise positioning is possible with simple control. On the other hand, servo motor-driven types employ feedback control for specifying target positions or speeds, offering dynamic responsiveness. The actuator type is determined according to the two types of motor.
Electric actuators are categorized into the following five main types according to their driving methods and functions.
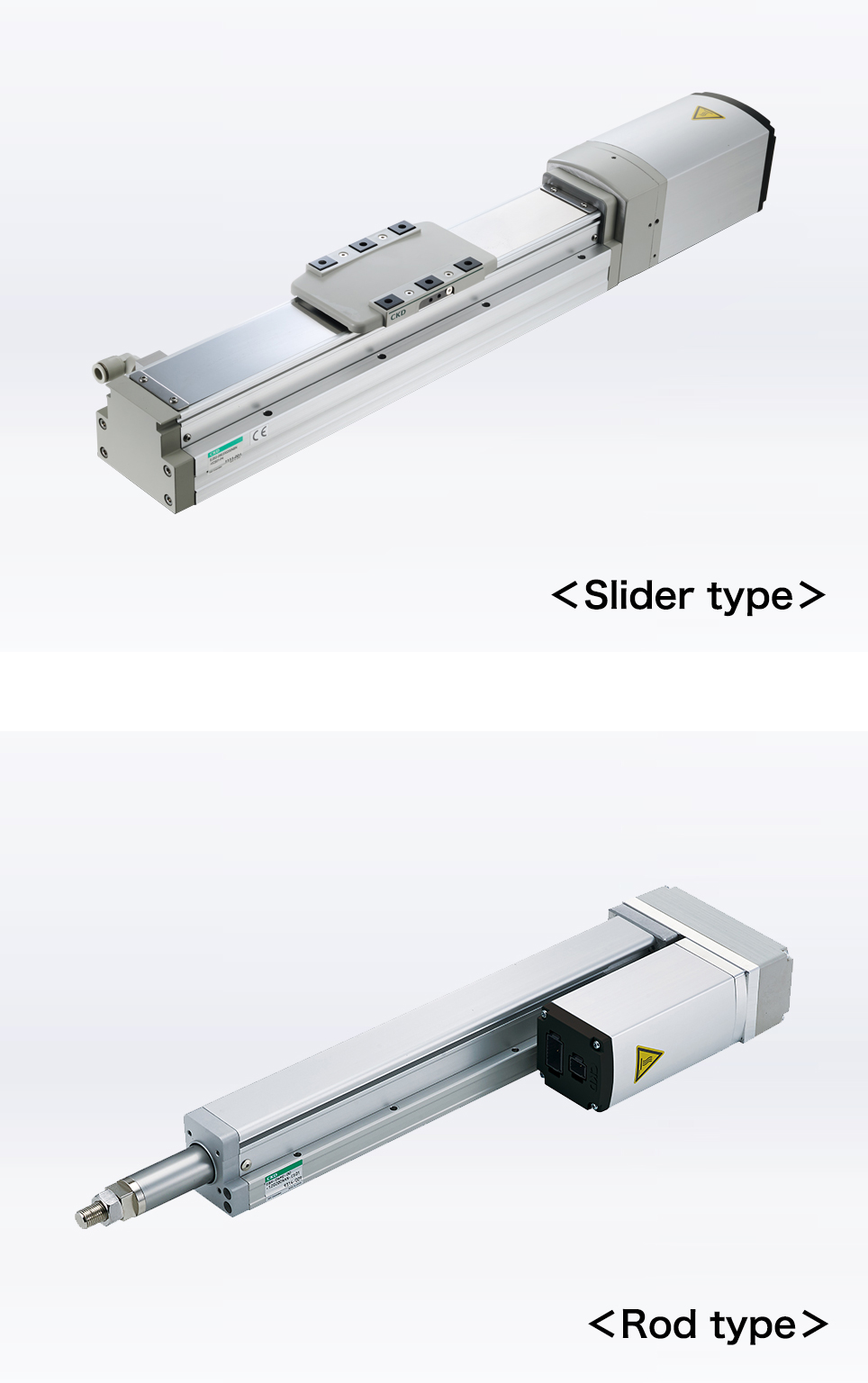
Slider and Rod types
Both convert motor rotational force into linear motion, but differ structurally. The slider type moves the slider linearly, mainly using ball screws and linear guides. Due to the high positioning accuracy and fast response time, this product is mainly used in general transport processes and assembling machines.
For the rod type, a ball screw is used mainly to expand and contract the piston rod. Used for press fitting processes and lifting applications, etc., since the piston rod contracts and is compatible with offset workpieces with built-in guides.
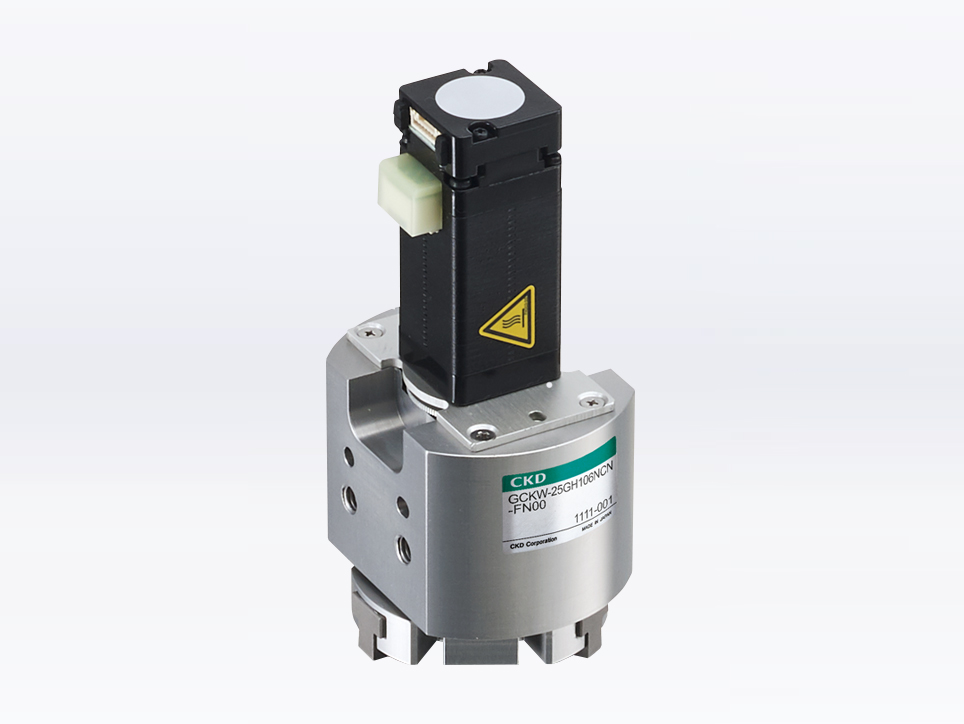
Gripper type
Electric actuator for gripping workpieces. Generally there are two-finger and three-finger types, the former is suitable for gripping square workpieces and the latter for gripping round workpieces.

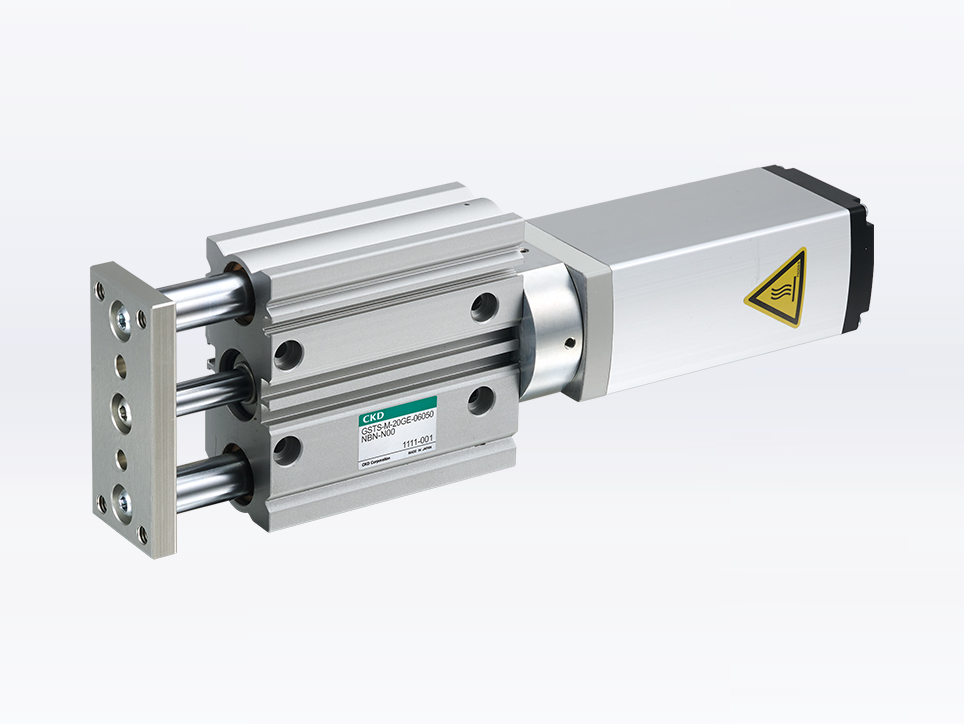
Guided type
Electric actuator equivalent to a pneumatic components guided cylinder. High rigidity and durability are achieved by using the same body as the pneumatic components.

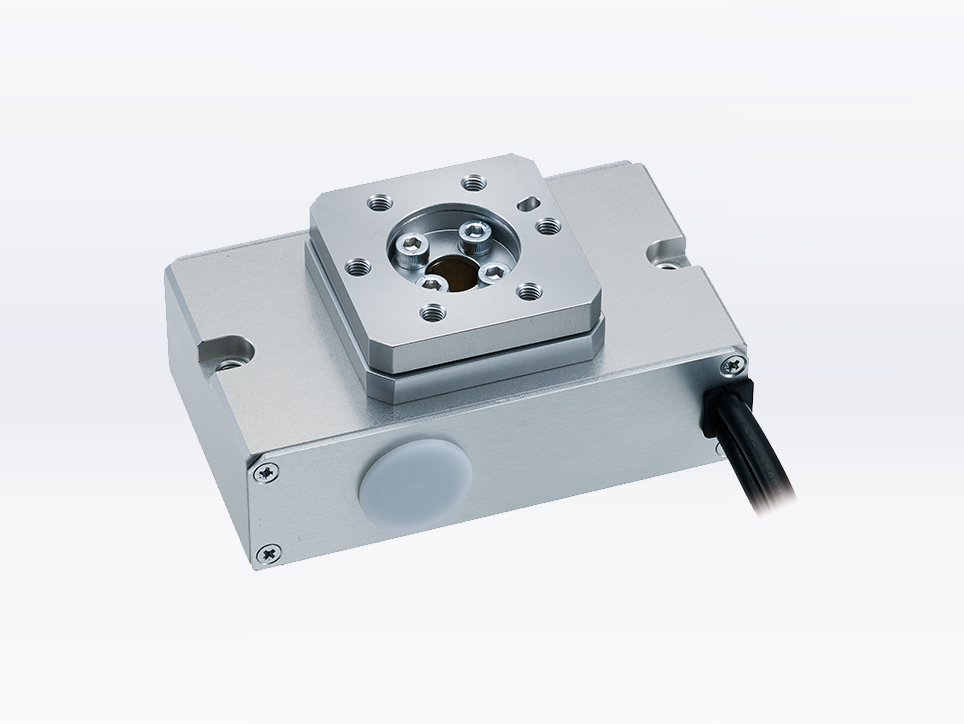
Rotary type
Electric actuator that can rotate. Multi-point positioning during rotation, reverse operation, indexing operation, etc. Acceleration and deceleration settings enable soft starts and stops, eliminating the need for shock absorbers.

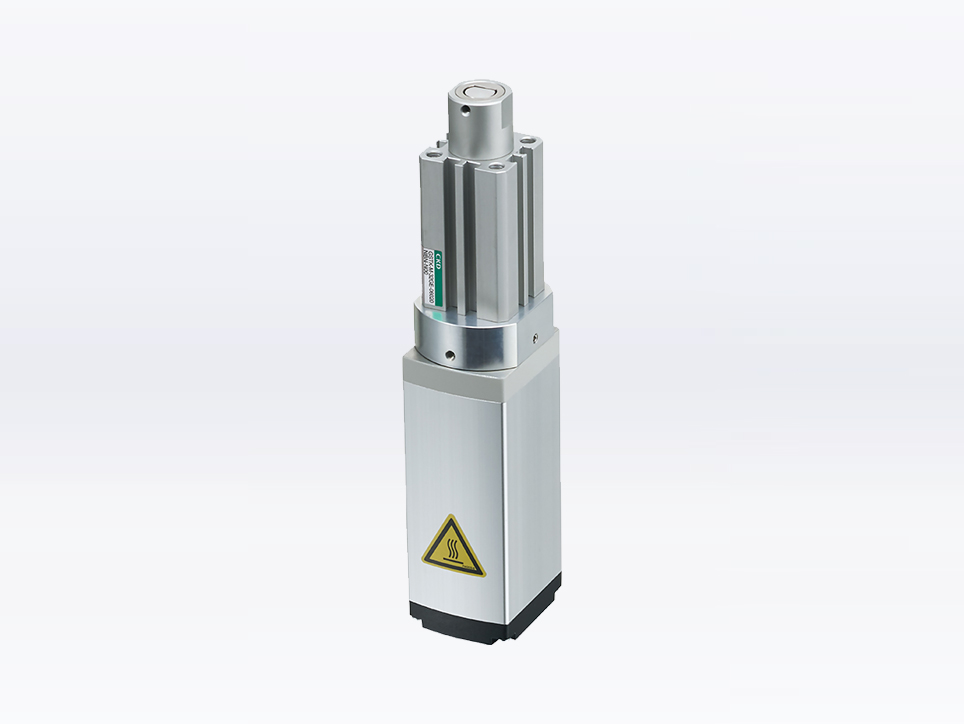
Stopper-type
Electric actuators for stopping the workpiece. These actuators are utilized to temporarily stop products flowing on a conveyor for operations such as press-fitting or inspection.

Criteria for Selecting Electric Actuators
How should one select the appropriate electric actuator? Consider the following points during selection:
Payload
Payload is the weight that can be transported. As the payload increases, the actuator and motor sizes that are required will generally increase. Select an actuator that supports the payload according to the application.
Stroke
Stroke is the operable length of the actuator. As it defines the range of motion, ensure the chosen actuator meets the necessary operational range.
Positioning repeatability
This pertains to the error when repeatedly positioning to the same spot from the same direction. Operations requiring precise positioning demand high-accuracy actuators, so select the motor type and drive method based on your requirements.
Speed
The operation speed of an actuator directly impacts productivity. The necessary speed is determined by the ability to perform within the set cycle time. For high-speed operations, choose an actuator that meets the required velocity.
Operating Environment
The operating environment of electric actuators may include temperature, humidity/water (atmosphere, direct application), chemical liquids (atmosphere), and dust. For temperature and chemicals, check the materials used in the electric actuator. For water and dust, verify the protection level.
Characteristics of Electric Actuators
Advantages:
Benefits of electric actuators include the following:
High efficiency: Generally, electric actuators are considered more efficient than pneumatic equipment. They tend to require less energy for the same operations, contributing to energy savings.
Number of positioning points:Normally, the air cylinder can only be positioned at the end of a stroke (2 points). However, since the electric actuator operates by a motor, it can stop at any position (multiple points).
Positioning accuracy: Electric actuators have ball screws and slide screws. Equipped with ball screws or lead screws, electric actuators can achieve high precision positioning mid-stroke, depending on the ball screws or motor's resolution.
Speed Adjustment: Electric actuators can vary operation speed mid-stroke, allowing for acceleration or deceleration as needed.
Disadvantages:
Compared to air cylinders, the initial cost tends to be higher for electric actuators. The control system is also more complex, requiring more specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance. Attention is necessary as some may have lower resistance to water or dust than air cylinders.
Drive components other than electric actuators
Compensating for the disadvantages of electric actuators drive components include air cylinders. Air cylinders are generally cheaper, smaller and lighter than electric actuators. It can be a more suitable choice for limited budgets, space, or simple reciprocating motions between two points. The air cylinder is also relatively resistant to harsh environmental conditions, making it suitable for use in situations where easy ON/OFF control is required. Consider alternatives to electric actuators depending on the application and operating environment.
CKD's Recommended Selection Method for Electric Actuators by Process
What processes do you recommend electric actuators for? We will explain the conditions under which the electric actuator is suited for the next process.
Handling Process
The handling process is the process of gripping the workpiece.
Recommended points for electric actuators!
・Soft handling
When working with soft materials, excessive gripping force can deform the workpiece. However, grippers (electric actuators) allow for adjustable gripping force, making them suitable for handling soft materials. Their stroke can also be adjusted according to the workpiece size, enabling versatility across various types of workpieces.
Conveyance Process
This involves the horizontal or vertical transport of handled workpieces.
Recommended points for electric actuators!
・High-precision multi-point positioning
Multipoint positioning without pneumatic components is possible with an electric actuator. An electric actuator is suitable for high-precision positioning of three or more locations.
Clamping Process
This process involves temporarily fixing the workpiece on the line for operations such as press-fitting, inspection, and assembly.
Recommended points for electric actuators!
・Adjustable clamping speed
・Soft clamp
Electric actuators are recommended for applications requiring mid-stroke speed adjustments during clamping. Their ability to adjust clamping force and reduce speed at the moment of clamping also makes them suitable for soft workpieces.
Press Fitting Process
A process involving two workpieces being pressed together with strong force.
Recommended points for electric actuators!
・Control of thrust and press-fitting speed
Although pneumatic devices may seem suited for their ability to generate significant force, electric actuators are preferable for applications requiring adjustable thrust and press-fitting speeds. They also offer the ability to verify if the desired position (depth) has been achieved.
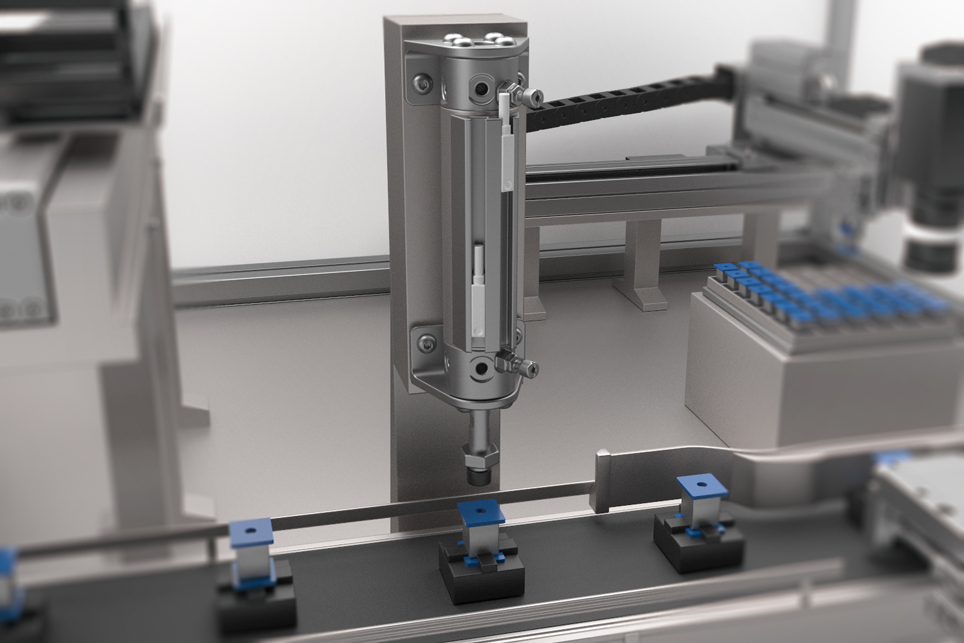
Oscillating Process
The motion of swinging back and forth between two points at a set angle, like a pendulum, to transport workpieces. While the conveyance process involves linear motion, the oscillate process involves rotary motion.
Recommended points for electric actuators!
・Multi-point positioning
Rotary-type electric actuators have advantages in multi-point positioning, capable of stopping at several points and facilitating dividing actions, making them beneficial for rotary movements.
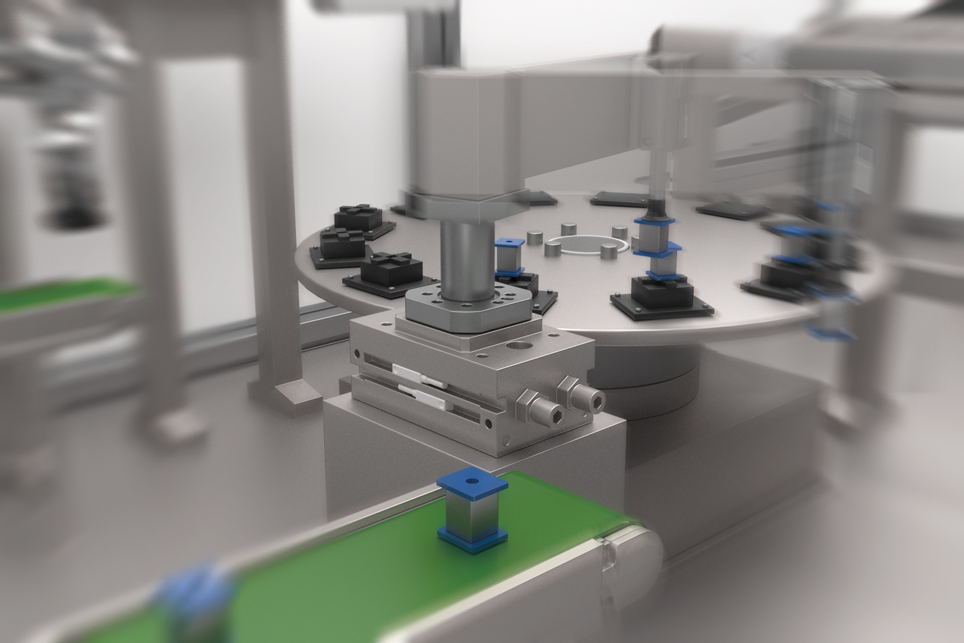
CKD's Electric Actuators
Supporting system automation and energy conservation in the industrial sector
Historically, factory automation has evolved around low-cost, easily automated pneumatic equipment. Cost-effective pneumatic devices have reduced the costs of devices and produced goods, supporting end-users' competitive pricing. However, with the growing awareness of SDGs in recent years, manufacturing that considers environmental issues and utilizes electric actuators is becoming socially accepted. It is important to note that pneumatic and electric actuators each have their strengths and weaknesses. Being a provider of both types of products, CKD is uniquely positioned to propose the optimal solutions tailored to customers' applications and objectives.
CKD product lineup
CKD has a wide range of rotary actuator, including DD motors and Mechanical indexers. In addition, we have a wide range of electric actuator variations, and we have also released SCARA robots and image processing software. CKD is engaged in the development of products that meet market demands, such as by being the first to develop a series of products specialized for specific industries, such as food and rechargeable batteries.
Air & Electric Motion: Best Mix
CKD develops and manufactures both air cylinders and electric actuators. By evaluating the functions and costs of each, CKD proposes optimal solutions that leverage the best features of both air and electric solutions. Feel free to consult us.
For more information on CKD's electric actuators, follow this link.